Doug Woods
Memories






woodsdou@oregonstate.edu
Resume
I received my Ph.D. in Nuclear Engineering from the School of Nuclear Science and Engineering at Oregon State University. My major advisor is Todd Palmer.
Research
We have demonstrated the feasibility of high-order discontinuous Galerkin finite element (DGFEM) radiation transport using meshes with curved surfaces using the open source finite element library MFEM. The image below illustrates a mesh with 3rd order polynomial curved surfaces.
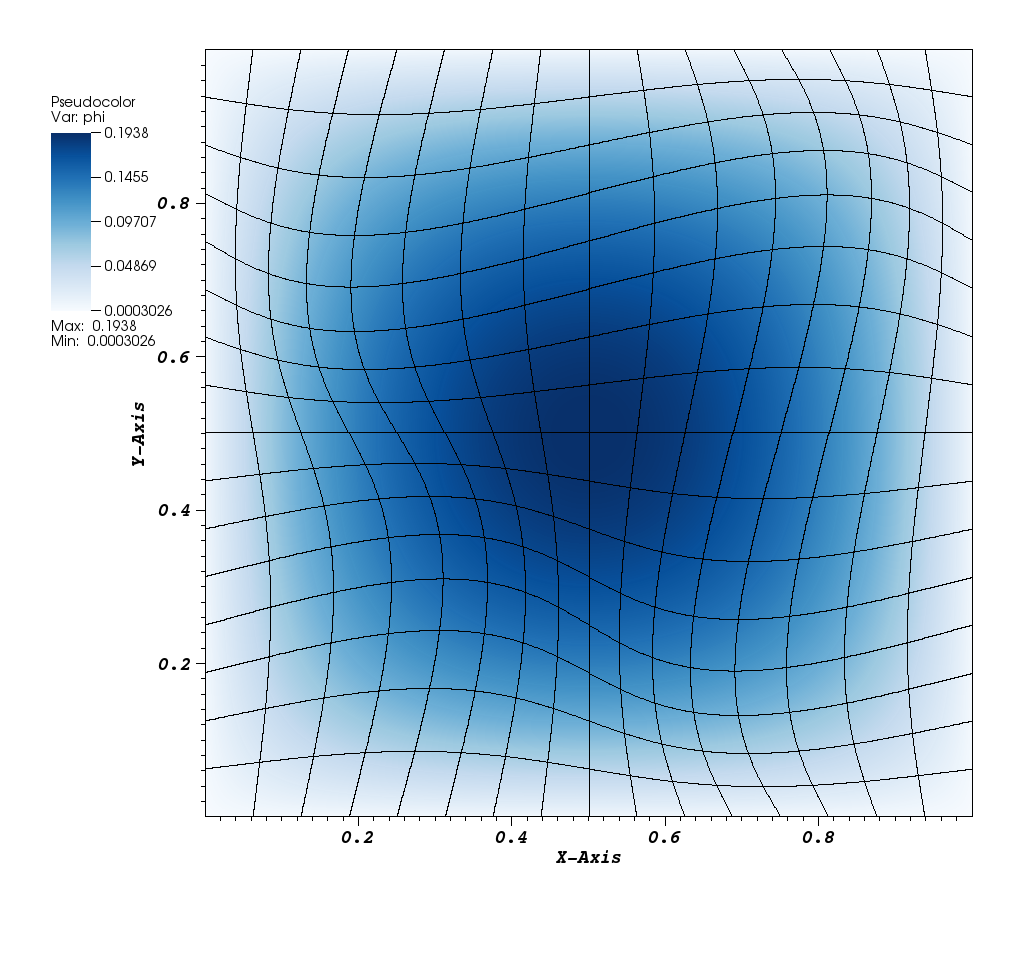
Accuracy
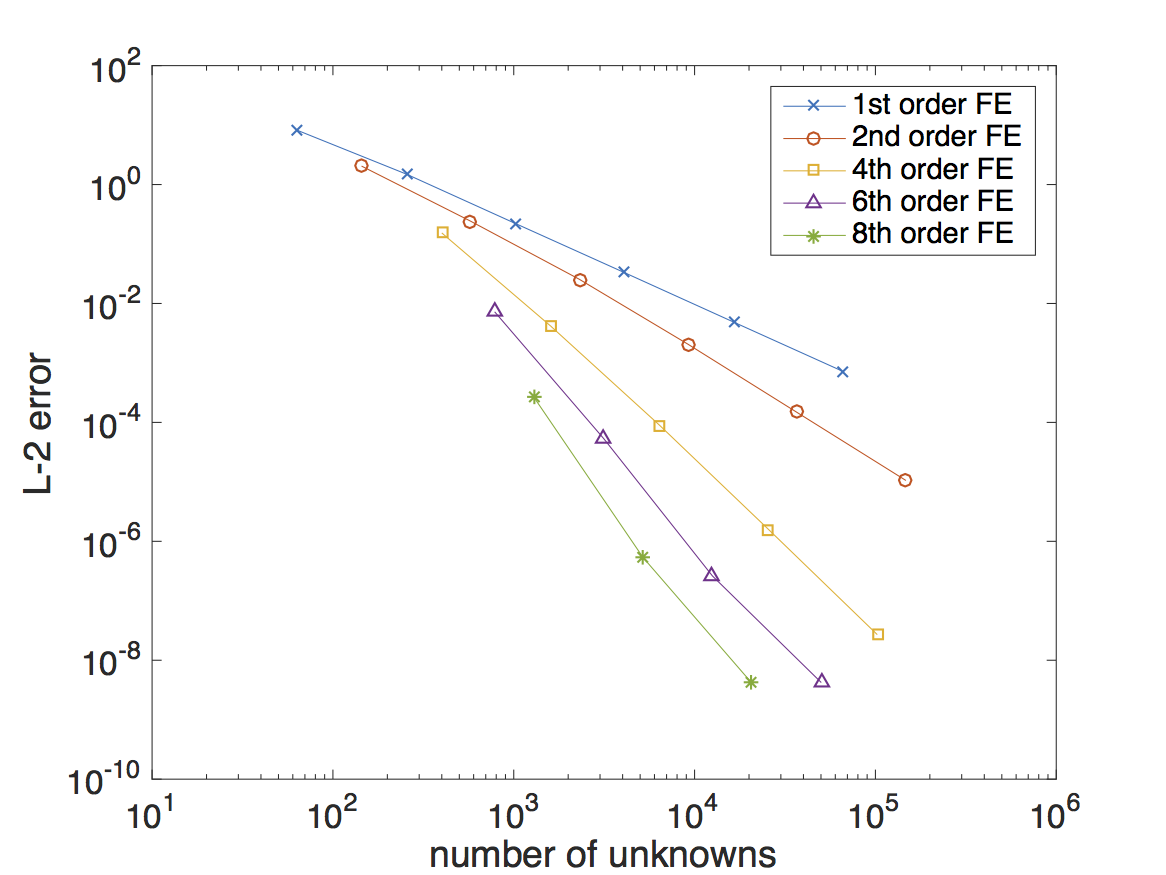
With mesh refinement and/or increasing the finite element order (i.e. increase the number of degrees of freedom), we see solutions converging to the manufactured solution. The data points on the following image [6] show errors between the DGFEM transport solution and the analytic MMS solution. Lines connect data points that were calculated using the same finite element order. The slope of the lines indicate the rate of convergence is (p+1). Remarkably, curvature of the mesh has little influence on the convergence rates.
Diffusion Limit
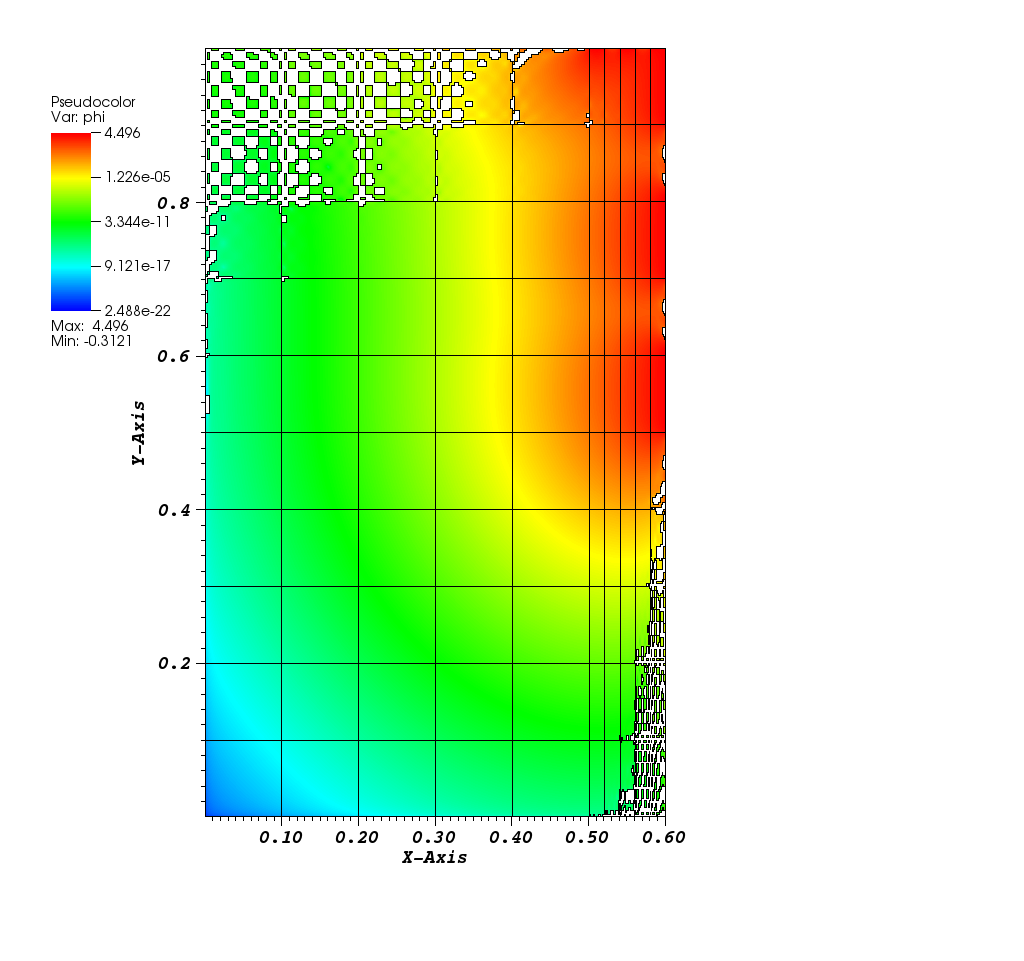
Diffusion limit calculations can exhibit unphysical oscillations. If the solution is near zero, the oscillations will cause the solution to drop below zero as seen by white space in the image below. In the context of thermal radiation transport, negative fluxes result in negative temperatures, which can lead to the equations of state calculating negative densities and pressures. We smoothly model this exponential solution, which changes over 22 orders of magnitude.
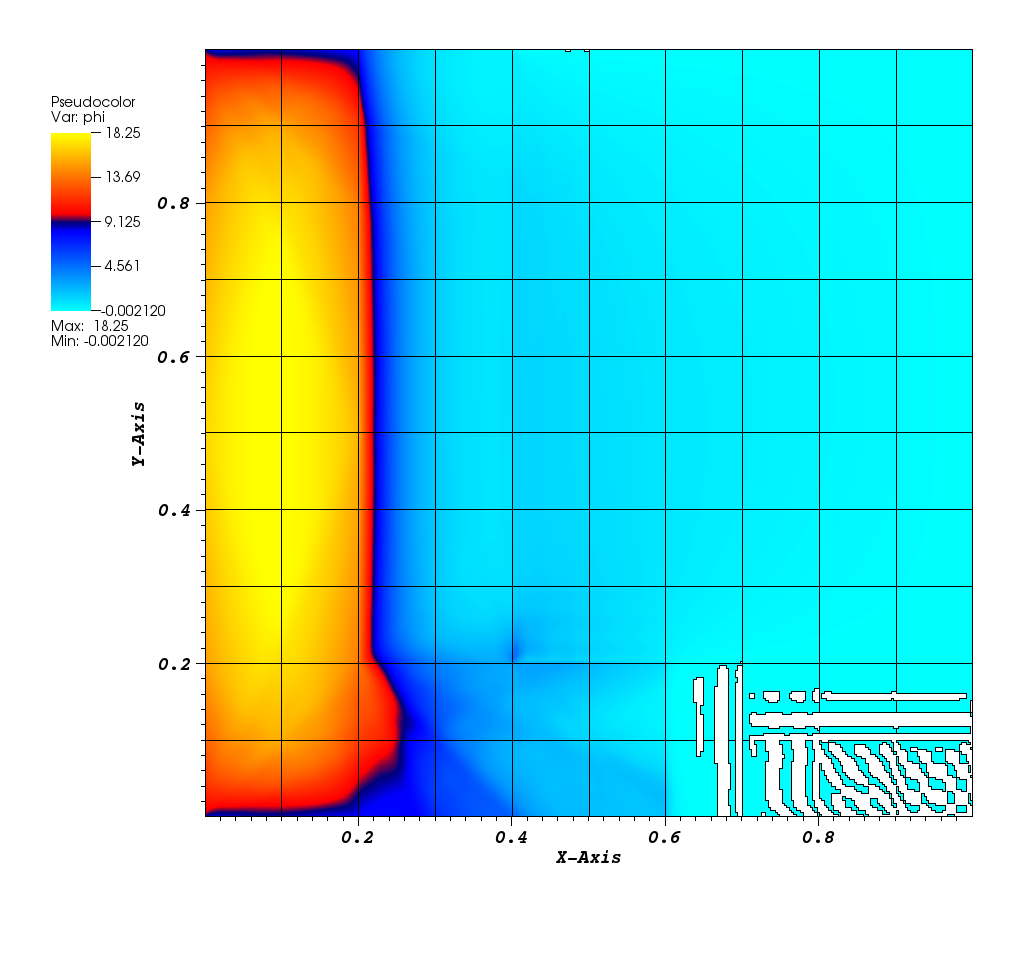
These oscillations can also be seen in problems with varying material cross sections. The image below is the solution to a heterogeneous problem with cross sections ranging several orders of magnitude, similar to thermal radiation transport problems of practical interest. Oscillations are primarily seen in highly absorbing region.
Diffusion Synthetic Acceleration
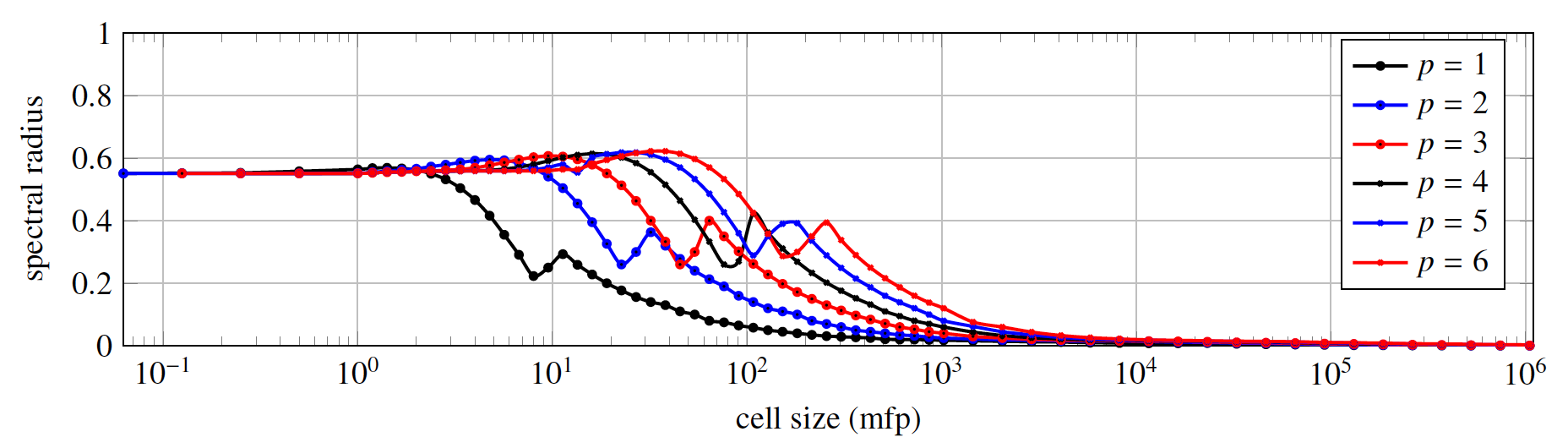
The source iteration (SI) method converges arbitrarily slowly for highly scattering and diffusive problems. We implement the modified interior penalty (MIP) DSA developed by Wang and Ragusa (2010) to accelerate the SI. In the image below, we investigate the convergence rates for various finite element orders. We see accelerated convergence for all cell sizes. Again, curvature of the mesh surfaces has relatively little influence on the spectral radii.
R-Z Geometry Spatial Discretization
We implemented the high-order DFEM spatial discretization in R-Z geometry and tested it with several problems.
Spatial Convergence
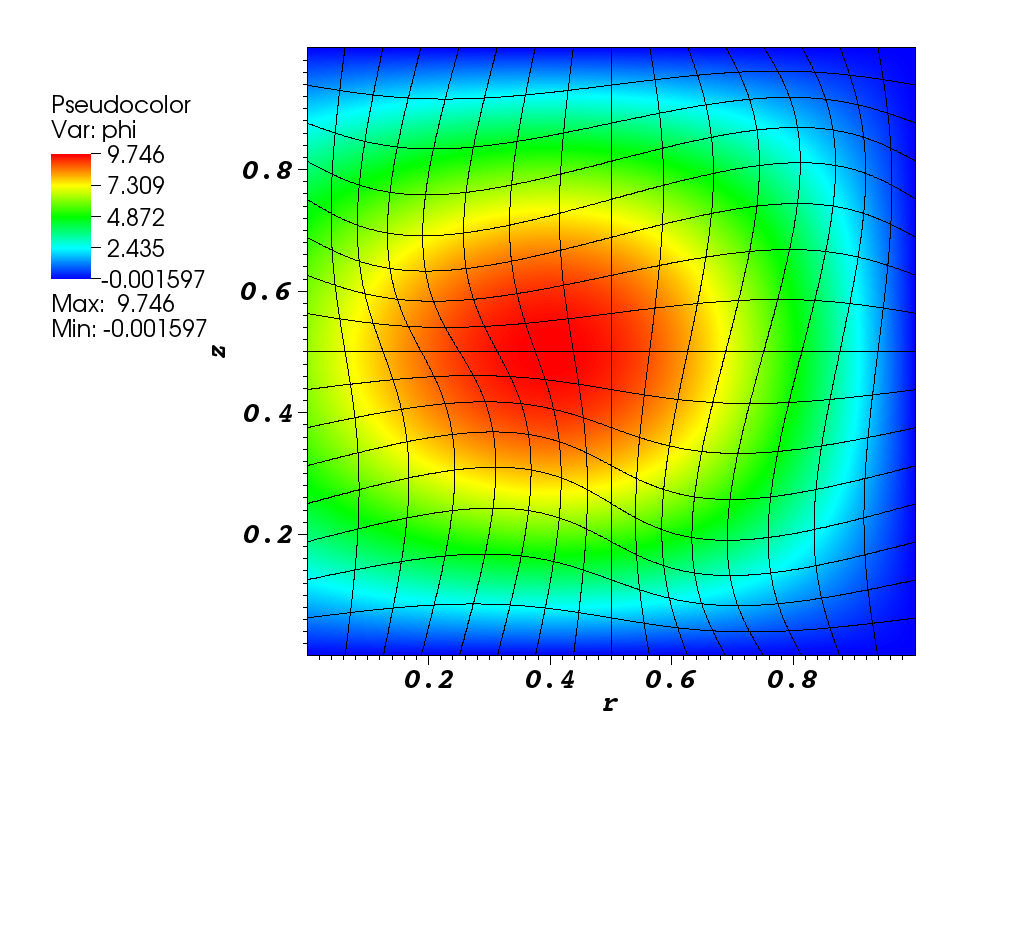
Spatially discretizing the discrete ordinates transport equation in R-Z geometry has been successful using low-order finite elements. We demonstrated that high-order finite elements preserves the O(p+1) convergence on smooth solutions as did the low-order methods.[1]
Axisymmetry Preservation
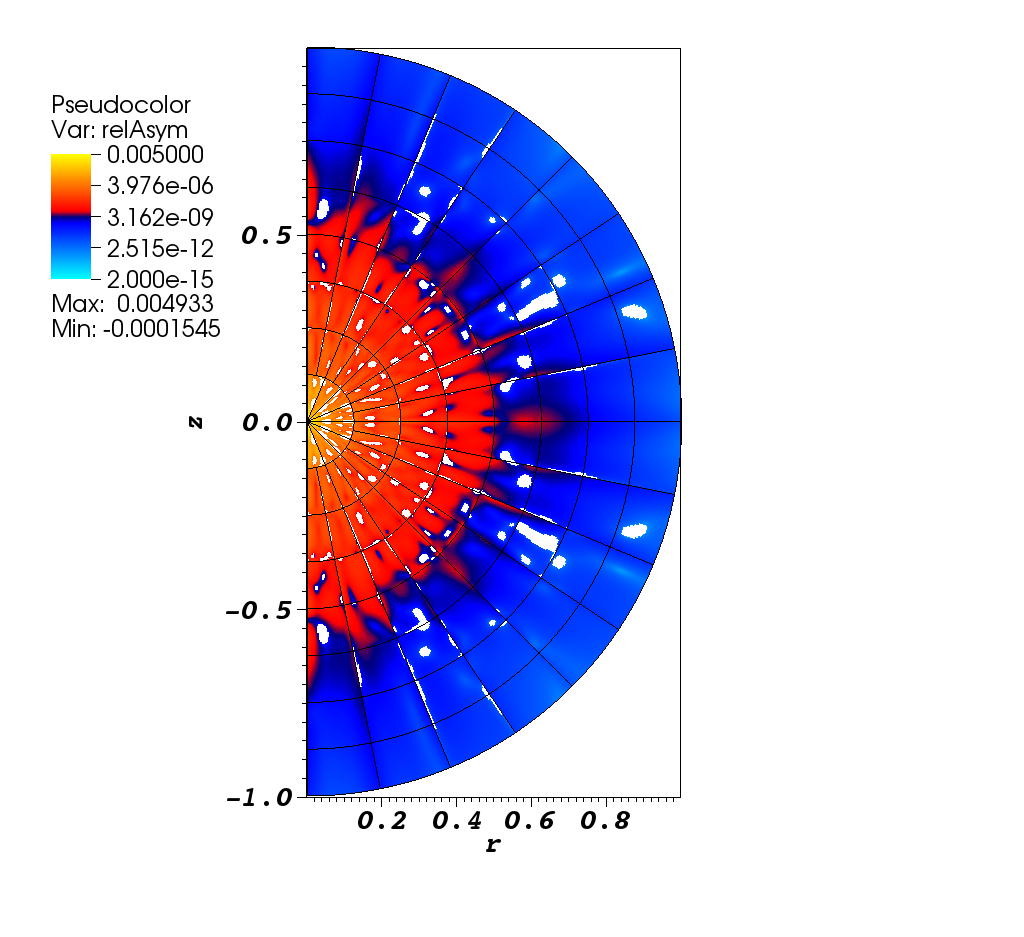
Using 4th order finite elements and S12 level-symmetric angular quadrature, we demonstrate the amount of symmetry preservation on a 2nd-order mesh. The image shows the error relative to the nodal errors at the same spherical radius (i.e., same distance from the origin). This study informed us that spatial refinement and higher-order finite elements increase the amount of symmetry, whereas the Sn order has little effect. The addition of mesh curvature only benefits low-order (i.e., 1st-order) methods.[3]
Publications
-
Douglas N. Woods, and Todd S. Palmer, “R-Z Geometry Discrete Ordinates Radiation Transport using Higher-Order Finite Element Spatial Discretizations on Meshes with Curved Surfaces”, Journal of Computational and Theoretical Transport, In Review.
-
Douglas N. Woods, Thomas A. Brunner, and Todd S. Palmer, “High Order Finite Element SN Radiation Transport on Meshes with Curved Surfaces”, Nuclear Science and Engineering, In Review.
-
Douglas N. Woods. Discrete Ordinates Radiation Transport using High-Order Finite Element Spatial Discretizations on Meshes with Curved Surfaces, PhD Dissertation, Oregon State University, 2018.
-
Douglas N. Woods, and Todd S. Palmer, “Diffusion Synthetic Acceleration for High Order SN Transport on Meshes with Curved Surfaces”, Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 116, 639-642 (2017).
-
Douglas N. Woods, Thomas A. Brunner, and Todd S. Palmer, “High Order Finite Elements SN Transport in X-Y Geometry on Meshes with Curved Surfaces”, Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 114, 377–380 (2016).
-
Douglas N. Woods, “High Order Finite Elements SN Transport in X-Y Geometry on Meshes with Curved Surfaces in the Thick Diffusion Limit”, Masters Thesis (2016).
Presentations
- PhD Dissertation Defense, Corvallis, OR, June 2018
- 2018 ANS Student Conference, Gainesville, CA, April 2018
- ICTT-25, Monterey, CA, October 2017 (Abstract/Presentation)
- ANS Summer Meeting, San Francisco, CA, June 2017
- OSU College of Engineering Graduate Research Showcase, Corvallis, OR, February 2017
- American Nuclear Society Summer Meeting, New Orleans, LA, June 2016
- OSU Graduate Research Expo, Portland, OR, March 2016
- OSU Graduate Research Expo, Portland, OR, March 2015
- ANS Student Conference, Boston, MA, April 2013
- ANS Student Conference, Las Vegas, NV, April 2012
Other Projects
Personal interests
Soccer, snowboarding, motorcycling, sailing, rock climbing, hiking, camping, reading, traveling
